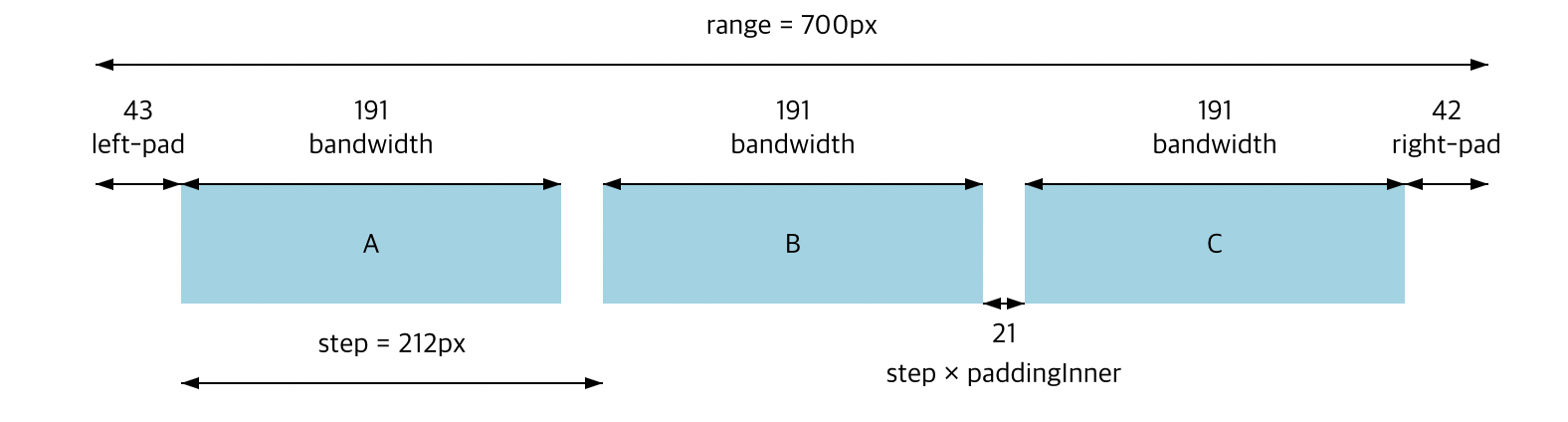
children을 포함하는 계층 데이터
D3에서 사용할 데이터를 정의할 때, 부모-자식 관계를 정하기 위해서 children을 반드시 포함시켜야 합니다. children에 자식 노드를 추가하면서 계층 데이터 형태로 구성할 수 있습니다.
interface TreeData {
id: string;
children?: TreeData[];
}
const TREE_DATA: TreeData = {
id: 'Chaos',
children: [
{
id: 'Gaia',
children: [
{
id: 'Mountains',
},
{
id: 'Pontus',
},
{
id: 'Uranus',
},
],
},
{
id: 'Eros',
},
{
id: 'Erebus',
},
{
id: 'Tartarus',
},
],
};
기본적인 Hierarchy 객체 생성하기
hierarchy 함수를 호출하면 D3에서 정의한 HierarchyNode 타입의 객체가 리턴되며, 각각의 프로퍼티에 대한 설명은 다음과 같습니다.
- children : 자식 노드들
- data : 사용자가 정의한 데이터
- depth : 트리에서 자신의 노드의 깊이
- height : 자식 노드의 최대 깊이
- parent : 부모 노드 없으면 null
const root = hierarchy<TreeData>(TREE_DATA);
console.log(root);
{
children: [Node, Node, Node, Node],
data: {id: "Chaos", children: Array(4)}
depth: 0,
height: 2,
parent: null
}
레이아웃 객체 생성하기
앞에서 생성한 객체를 가지고, D3에서 제공하는 레이아웃 객체를 생성할 수 있습니다. 아래는 트리를 그리기 위한 레이아웃 객체를 생성하는 코드이며, HierarchyNode 타입을 상속한 HierarchyPointNode 타입의 객체로 변경됩니다.
x, y 프로퍼티가 추가된 것을 확인할 수 있으며, 캔버스나 SVG로 무엇인가 그릴 때, 해당 값을 그대로 사용하면 됩니다.
HierarchyNode 타입을 상속하는 타입은 HierarchyPointNode 외에도 HierarchyRectangularNode, HierarchyCircularNode 타입이 있습니다.
const treeLayout = tree().size([WIDTH, HEIGHT]);
treeLayout(root);
console.log(root);
{
children: [Node, Node, Node, Node],
data: {id: "Chaos", children: Array(4)}
depth: 0,
height: 2,
parent: null,
x: 233.33333333333334,
y: 0
}
로우셋을 계층 데이터로 변환하기
때로는 children 프로퍼티가 포함되어있지 않고, 부모 키만 알고 있는 데이터를 가지고 있을 수 있습니다.
interface RowData1 {
id: string;
parentId?: string;
}
interface RowData2 {
id2: string;
pid?: string;
}
const ROW_DATA_1: RowData1[] = [
{ id: 'Chaos' },
{ id: 'Gaia', parentId: 'Chaos' },
{ id: 'Eros', parentId: 'Chaos' },
{ id: 'Erebus', parentId: 'Chaos' },
{ id: 'Tartarus', parentId: 'Chaos' },
{ id: 'Mountains', parentId: 'Gaia' },
{ id: 'Pontus', parentId: 'Gaia' },
{ id: 'Uranus', parentId: 'Gaia' },
];
const ROW_DATA_2: RowData2[] = [
{ id2: 'Chaos' },
{ id2: 'Gaia', pid: 'Chaos' },
{ id2: 'Eros', pid: 'Chaos' },
{ id2: 'Erebus', pid: 'Chaos' },
{ id2: 'Tartarus', pid: 'Chaos' },
{ id2: 'Mountains', pid: 'Gaia' },
{ id2: 'Pontus', pid: 'Gaia' },
{ id2: 'Uranus', pid: 'Gaia' },
];
D3에서는 children과 마찬가지로 id와 parentId 프로퍼티를 스스로 인식합니다. stratify 함수를 사용하면 hierarchy 함수와 동일한 객체를 리턴하게 됩니다.
하지만 데이터 id와 parentId 프로퍼티가 포함되어 있지 않다면 id와 parentId 메소드를 통해 부모-자식 관계를 설정할 수 있습니다.
const root1 = stratify<RowData1>()(ROW_DATA_1);
const root2 = stratify<RowData2>()
.id((data) => data.id2)
.parentId((data) => data.pid)(ROW_DATA_2);
console.log(root2);
{
children: [Node, Node, Node, Node],
data: {id: "Chaos", children: Array(4)}
depth: 0,
height: 2,
parent: null
}
Hierarchy 객체의 메소드 소개
계층 데이터를 쉽게 핸들링할 수 있는 몇가지 메소드들을 소개합니다.
const chaos = root2;
const gaia = chaos.children[0];
const pontus = chaos.children[0].children[1]
const tartarus = chaos.children[3];
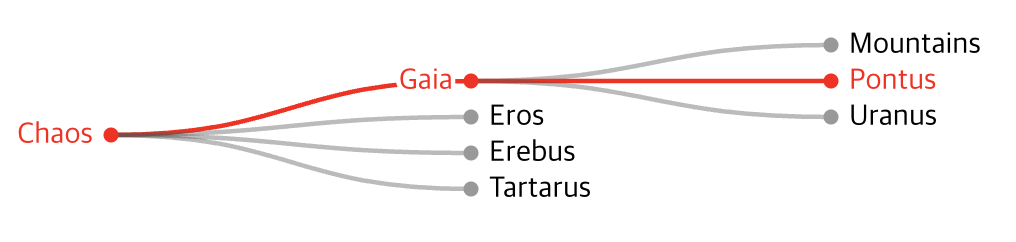
ancestors
자신을 포함하여 루트까지 모든 부모 노드의 배열을 반환합니다.
gaia.ancestors();

pontus.ancestors();
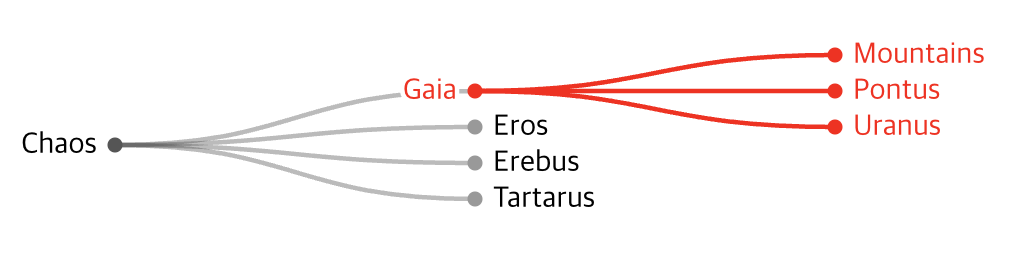
descendants
자신을 포함하여 모든 자식 노드의 배열을 반환합니다.
gaia.descendants();
leaves
해당 노드의 자식 중에 자식이 없는 노드의 배열을 반환합니다
gaia.leaves();

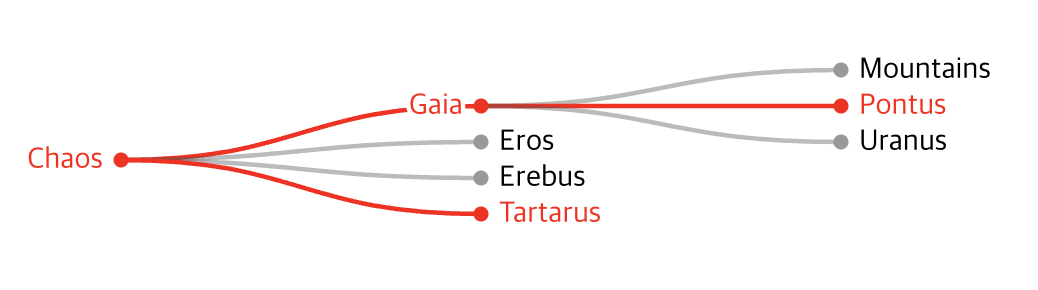
path
해당 노드부터 대상 노드까지 연결된 모든 노드의 배열을 반환합니다.
Tartarus -> Chaos -> Gaia -> Pontus
tartarus.path(pontus);
links
해당 노드의 자식 링크를 나타내는 객체 배열을 반환합니다. 각 링크 객체의 target은 자식이고, source는 부모입니다. gaia의 자식 노드인 mountains, pontus, uranus를 target으로 가진 HierarchyPointLink 타입을 가지는 배열을 리턴합니다.
앞에서 트리 레이아웃을 사용했기 때문에 HierarchyLink가 아닌 HierarchyPointLink 타입의 객체를 리턴합니다. 그 밖에도 HierarchyCircularLink, HierarchyRectangularLink 타입이 있습니다.
gaia.links();